Toxic Mold In Your Home A Guide For Consumers
$24.00
- Examples of where hidden mold can grow
- How to understand a mold inspection report and interpret the sample results
- How to use the inspection report to tell if your home has mold
Out of stock
Be An Informed Consumer
Get the facts about:
How to find hidden mold in your home
How to understand a mold inspection report, and the sample results
How to use the inspection report to tell if your home is mold-contaminated - and - if occupant exposures are acceptable
Dr. Spurgeon has performed thousands of mold inspections on both residential and commercial properties. As a result of those inspections, it became obvious that the typical consumer did not have the knowledge necessary to participate in the inspection process. This book attempts to help consumers whose homes have been affected by water damage to become informed consumers of a mold inspection.
There are two objectives of a mold inspection. The first is to determine if the home is contaminated with mold; and the second is to determine if occupant exposures are acceptable. Unfortunately, having your home inspected for mold can be like buying a used car. The salesman knows the condition of the car, but there is little guidance available to the consumer.
When having your home inspected, the mold inspector may understand what’s happening, but the consumer is rarely an informed consumer; and often does not understand either the inspection process or how to interpret the sample results. The topics discussed in this book include:
- How do I know if my home may have mold?
- Do men and women respond to mold differently?
- Mold and immune-compromised occupants
- How to find hidden mold in your home
- Your options for responding if your home does have mold
- Understanding the parts of a mold inspection
- What types, and where, should mold samples be collected
- Options and costs for analyzing mold samples
- Understanding the sample results in a mold report
- How much mold in your home is too much?
Besides conducting thousands of mold inspections, Dr. Spurgeon has presented numerous courses teaching inspectors how to perform mold inspections, collect samples, and to interpret sample results.
Dr. Spurgeon has also served as an expert witness in hundreds of mold cases.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABBREVIATIONS, DEFINITIONS, AND CONCEPTS vii
1. Abbreviations vii
2. Definitions vii
3. Concepts viii
1. INTRODUCTION 1
1.1. Why Read this Book? 1
1.2. Why Just Discuss Mold? 1
1.3. How do I know if mold may be a problem? 2
1.4. When is indoor mold a problem? 3
1.5. What is an “indicator” mold? 5
1.6. What is a “toxic” mold? 6
1.7. Do men and women respond differently to mold? 6
1.8. Organ-transplant Patients, Immune-compromised Occupants 9
1.9. Factors Affecting Mold Growth 9
1.10. Humidity and Moisture Content 10
1.11. Stakeholders in the Inspection 11
2. DOES YOUR HOME HAVE HIDDEN MOLD? 13
2.1. Hidden Mold 13
2.2. Shower Heads 14
3. MANAGING THE MOLD IN YOUR HOME 33
3.1. The Occupant Exposure Model 33
3.2. Duration of Occupant Exposure 34
3.3. Removing Mold-Contaminated Materials 35
4. THE INSPECTION PROCESS 37
4.1. Phases in a Mold Inspection 37
4.2. Type of Inspection 37
4.3. Types of Materials 37
4.4. Possible Outcomes of an Inspection 39
5. COLLECTING MOLD SAMPLES 41
5.1. Why should Mold Samples Be Collected? 41
5.2. When Should Mold Samples Be Collected? 41
5.3. Who Should Collect Mold Samples? 42
5.4. What types of Mold Samples Should Be Collected? 42
5.5. Where Should Mold Samples Be Collected? 43
5.6. What are Reference and Control Samples? 43
5.7. Indoor Bacteria 45
6. ANALYZING MOLD SAMPLES 47
6.1. Introduction 47
6.2. Pricing 47
6.3. Cultured Samples 48
6.4. qPCR Samples 49
7. THE LABORATORY REPORT 51
7.1. Introduction 51
7.2. Tape Lift Samples 51
7.3. Total Airborne Fungal Spores 53
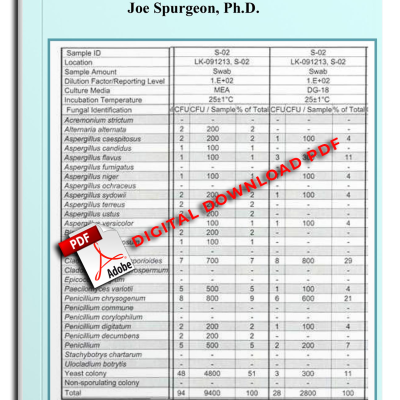
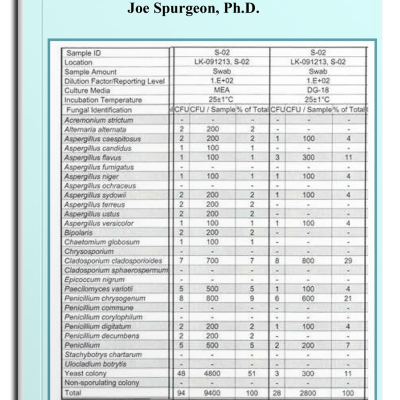
7.4. Surface Swab Samples 55
7.5. Carpet Dust Samples 58
8. HOW MUCH MOLD IS TOO MUCH? 61
8.1. Introduction 61
8.2. Comparison of Reference and Control Methods 61
8.3. Assessing Building Contamination 63
8.4. Assessing Occupant Exposure 64
8.5. Airborne Culturable Fungi 67